- Acknowledgements: The authors are thankful for the financial support from DOMCA S.A., the BioTic Granada Campus of International Excellence (Project mP_BS_2, CAPRILACT), and the research group FQM-302 (University of Granada, Spain).
- Authors: P. Abad, N. Arroyo-Manzanares, L. Gil, A.M. García-Campaña.
- Reference: J. Agric. Food. Chem. 65 (2017) 793-799.
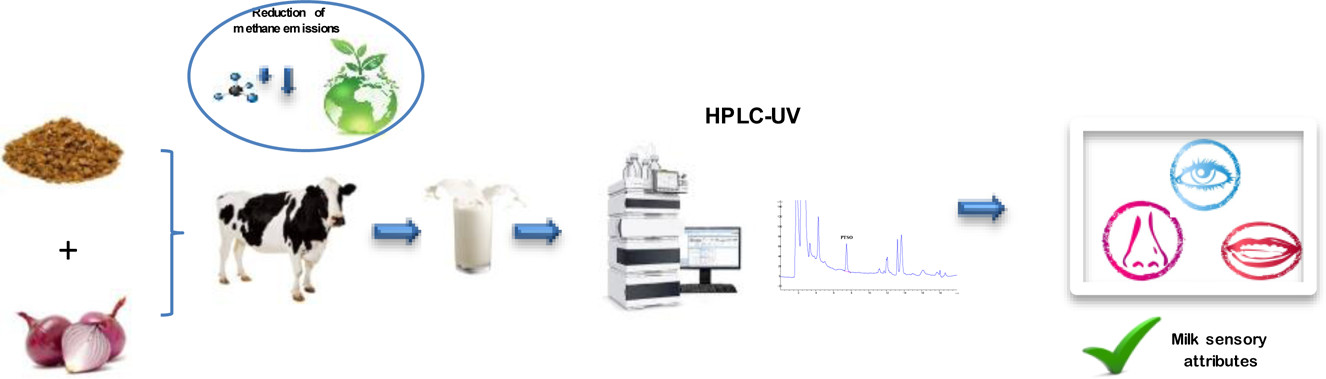
Onion extract is used as a feed supplement for the diet of dairy cows, acting as inhibitor of methane production; however, its properties could alter sensory attributes of milk. In this work, we propose a method to evaluate the influence of this extract on milk properties, using propyl propane thiosulfonate (PTSO) as a marker. PTSO is extracted using a quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe procedure and monitored by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. The method was applied to milk samples obtained from 100 dairy cows fed during 2 months with enriched feed. In addition, a milk tasting panel was established to evaluate the PTSO residue that should not be exceeded to guarantee milk sensory attributes. It was established that a value of PTSO lower than 2 mg kg–1 does not alter milk organoleptic properties. This fact makes onion extract an interesting alternative as a feed supplement to control the methane emissions without any influence on milk attributes.